How Smart Sensors Are Revolutionizing Pipeline Monitoring Systems, #12501
Owner
Description
What Are Smart Sensors?
Smart sensors are devices equipped with advanced sensing capabilities combined with microprocessors that can process data before transmitting it. Unlike traditional sensors, which merely collect raw data, smart sensors can perform tasks such as self-calibration, diagnostics, and wireless communication. This makes them ideal for complex and distributed systems like pipelines.
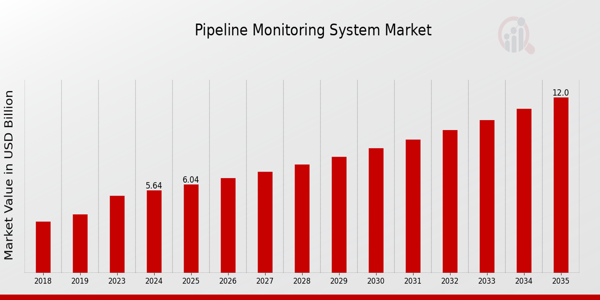
According to a Pipeline Monitoring System Market report, the industry is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
Key Benefits of Smart Sensors in Pipeline Monitoring
1. Real-Time Leak Detection
One of the most critical challenges in pipeline management is identifying and responding to leaks. Smart sensors can detect minute changes in pressure, temperature, acoustic signals, or flow rate, enabling them to identify potential leaks almost instantaneously. This rapid response drastically reduces the risk of environmental damage, financial loss, and safety hazards.
2. Predictive Maintenance
By continuously monitoring the health of the pipeline, smart sensors provide valuable data that can be used for predictive maintenance. Instead of relying on scheduled maintenance or responding to failures after they occur, operators can use sensor data to anticipate issues before they become serious—minimizing downtime and repair costs.
3. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Smart sensors allow for automated data collection and analysis, eliminating the need for manual inspections in many cases. This streamlines operations and frees up human resources for more strategic tasks. Additionally, smart sensors can optimize flow rates and pressure levels, helping to maximize throughput and energy efficiency.
4. Improved Safety and Regulatory Compliance
With smart sensors providing round-the-clock surveillance, operators can ensure their systems comply with increasingly stringent safety and environmental regulations. The availability of detailed logs and alerts also aids in audit readiness and incident investigations.
Technologies Powering Smart Sensor Systems
The smart sensors used in pipeline monitoring systems often incorporate several cutting-edge technologies:
-
Internet of Things (IoT): Enables connectivity and remote access to sensor data via the internet.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enhances data interpretation and anomaly detection, allowing for more accurate diagnostics.
-
Wireless Communication Protocols: Such as LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, and 5G, ensure that sensors in remote areas can still relay data effectively.
-
Energy Harvesting: Some smart sensors use energy harvesting to power themselves, extending operational life without frequent maintenance.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Several industry leaders have already embraced smart sensors:
-
TransCanada (TC Energy): Uses fiber-optic sensors along its pipelines to detect temperature and acoustic changes that may indicate leaks or structural issues.
-
Enbridge: Implemented a Smart Ball technology that travels through pipelines, collecting acoustic data to detect anomalies from within.
-
Shell and BP: Utilize smart sensors in offshore pipelines for real-time monitoring of subsea infrastructure, improving responsiveness and safety.
The Road Ahead
The adoption of smart sensors in pipeline monitoring is poised for exponential growth. As the cost of sensor technology continues to fall and connectivity becomes more widespread, even smaller operators will be able to deploy these systems. Future innovations may include integration with drones and robotics for inspections, or blockchain for secure data logging.











